Usage aiohttp admin
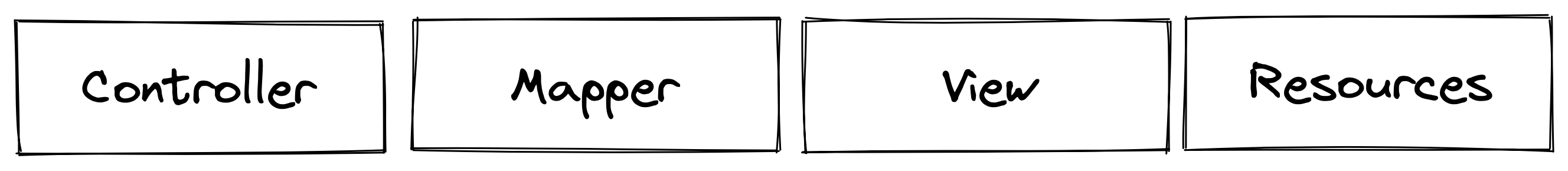
For the beginning let’s make a simple overview of architecture and main components. The aiohttp_admin has small list of main components which responsible for different function of admin interface:
resource - this component implement all method (get/delete/update etc) that need to communicate with databases. So, if you want to add support of database which is not exist right now on aiohttp_admin then can just create your resource object for that and all other components of admin interface will work with it togather without any problems
controller - in this component allocate business logic related with some model. What are fields we need to show on list view? How many items do we need to show on each list page? What is order we need to use by default? What do we need to do before/after create/update instance? How do models related? All these question about controller. Controller use resource to get access to database and mapper for validate input data from user.
mapper - this component responsible for validation and convert input data from user which will use for update or create instance.
view - this component responsible for represent result for user via some async web framework (now we use aiohttp but you can to implement views for other web framework and use other all components of aiohttp admin without any problems).
Let’s consider a simple example of books library. We have table of authors and books. Each book has one or more authors. Each author has one or more books. Relation between author and books is many to many and implement via a separate table. All these tables stores in the PostgreSQL but large book’s files allocated in the MongoDB.
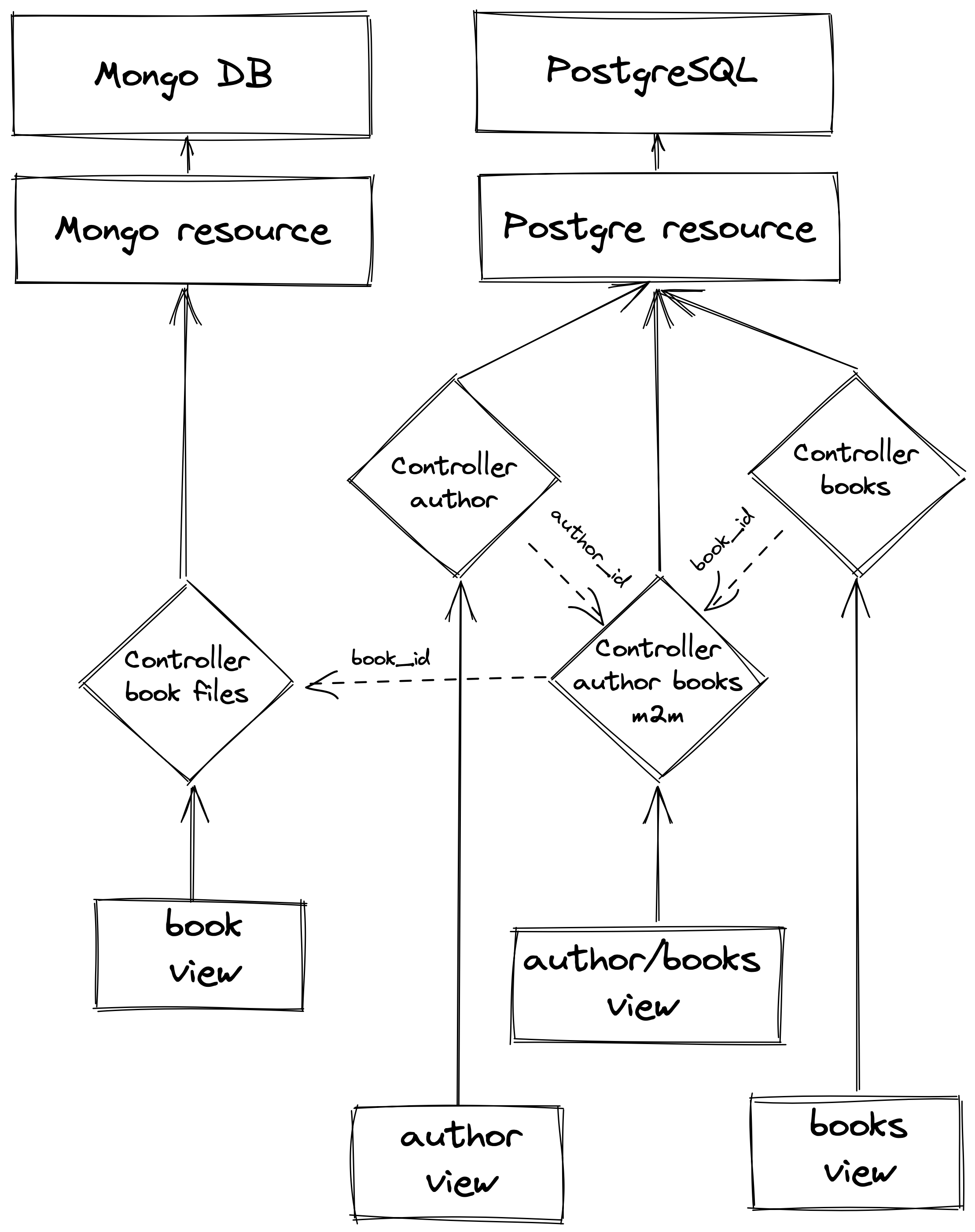
We can to see that relation between models implement on controller level and we can to bind models from different storages together.
Mappers
Mapper is schema for validation and converting data which income from user and use for create or update instances. You can create mapper in two ways.
Custom mappers
You can create your own mapper with custom fields:
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import Mapper
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
class UserMapper(Mapper):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
name = fields.StringField(required=True)
age = fields.IntField(default=18)
Mappers generator
If you create admin page for SQLalchemy or Umongo instances then you can generate mapping automatically by specifying models.
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers.generics import PostgresMapperGeneric
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
user = sa.Table('user', metadata,
sa.Column('name', sa.String(255)),
sa.Column('age', sa.Integer),
)
class UserMapper(PostgresMapperGeneric, table=user):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
pass
but if you want to rewrite some field you can do it some like that
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers.generics import PostgresMapperGeneric
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
class UserMapper(PostgresMapperGeneric, table=user):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
age = fields.StringField(required=True)
In this case generic will generate all fields for you but will use age field which you specify.
Fields
StringField, LongStringField, UrlImageField, UrlFileField, UrlField - field for represented string data.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
IntField, SmallIntField - field for represented integer data.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
FloatField - field for represented float data.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
DateTimeField, DateField - field for represented datetime data.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify (you can specify str or datetime/date object)
validators - list of validators
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
BooleanField - field for represented boolean data. If value contains ‘0’, ‘false’ or ‘f’ than value will be parse as False in other case as True.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
ChoicesField - add predefined values. If you have some finite list of values and want that this list will represented like select tag you need to use current field type.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
field_cls - field type which will represent selected value
choices - tuple of tuple with values. It might look like this [(‘admin title of value1’, ‘value1’), (‘admin title of value1’, ‘value2’)])
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
empty_value - need to to specify string which will show if a value is not set. By default it’s – empty –.
ArrayField - field for represented array data. Instances inside array must to have the same type. To specify this type you have to provide field_cls
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
field_cls - field type which will represent data type of items inside array
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
min_length, max_length - add validation related with min/max length of array
JsonField - field for represented data in json type format.
required - add validation for empty value if set to True
default - replace empty value if specify
validators - list of validators
primary_key - True if current field is a primary key
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers.generics import PostgresMapperGeneric
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
class UserMapper(PostgresMapperGeneric, table=user):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
GENDER_CHOICES = (
('male', "male"),
('female', "female"),
)
gender = fields.ChoicesField(
field_cls=fields.StringField,
choices=GENDER_CHOICES,
default='male'
)
In common you do not use mappers you need to create these only for internal usage for aiohttp admin but for a better understanding of why they are needed, let’s take a look at how they are used.
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import Mapper
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
class UserMapper(Mapper):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
name = fields.StringField(required=True)
age = fields.IntField(default=18)
Let’s try to validate wrong data
user_data = UserMapper({"age": '38'})
# return False because name is required
user_data.is_valid()
Now, try to check corrected data
user_data = UserMapper({"age": '38', "name": "mike"})
# return True because all is fine
user_data.is_valid()
print(user_data.data)
# {'name': 'mike', 'age': 38}
user_data.data return converting data in right type. We can see that string ‘38’ have been successful converting to int value 38.
Note
The primary key is required fields for any models when we wanna update instance but when we need to create instance we don’t know it (when a storage autoincrement it). For these purposes fields have primary_key property. If this property set to True and we try to create instance then mapper will ignore required errors related with current field. For that we need just specify skip_primary to True into is_valid method.
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import Mapper
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
class UserMapper(Mapper):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
id = fields.IntField(primary_key=True, required=True)
name = fields.StringField(required=True)
# False
UserMapper({"name": "Mike", "id": None}).is_valid()
# True
UserMapper({"name": "Mike", "id": None}).is_valid(skip_primary=True)
So when you don’t use generators for your models or rewrite primary key fields then don’t forget to specify primary key property.
Validators
We also can add custom validators for some particular field. Let’s consider case when we need to validate string value and check that this value has valid format for phone number. To do this we need to create validation function which raise exception if value is not corrected.
import re
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import Mapper
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers.exceptions import ValidationError
PHONE_REG = re.compile(r'^[0-9]{10,14}$')
def phone_validator(value):
if not PHONE_REG.match(value):
raise ValidationError("wrong phone format")
class UserMapper(Mapper):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
name = fields.StringField(required=True)
phone = fields.StringField(validators=[phone_validator])
# return False because '1234' is not valid format for a phone number
UserMapper({'name': 'Mike', 'phone': '1234'}).is_valid()
You also can to use standard validators from the aiohttp_admin2.mappers.validators module.
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import Mapper
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields
from aiohttp_admin2.mappers.validators import length
class UserMapper(Mapper):
"""Mapper for user instance."""
name = fields.StringField(validators=[length(max_value=10, min_value=3)])
Controllers
The controller is class that generate access to the your data based on some engine (Resource). Out of the box you have engines for different storages
PostgreSQL
MySQL
MongoDB (in progress)
but you actually can easy to add your own engine.
The controller is framework and database agnostic part of the admin. It’s mean that controller have not to know any about request/response, generation of urls, templates and so on. Also it have not to know about how to get/update/delete data from some database (this logic need to allocate into the resource class).
For the PostgreSQL, an easier way to create a controller is to use the PostgresController.
from aiohttp_admin2.controllers.postgres_controller import PostgresController
@postgres_injector.inject
class UserController(PostgresController, table=user):
mapper = UserMapper
name = 'user'
per_page = 10
For the MongoDB and the MySQL you can use MongoController and MySQLController apropriate.
The Controller need to have connection for engine. For this goal we need to inject connection by ConnectionInjector.
from aiohttp_admin2.connection_injectors import ConnectionInjector
postgres_injector = ConnectionInjector()
async def init_db(app):
# Context function for initialize connection to db
engine = await aiopg.sa.create_engine(
user='postgres',
database='postgres',
host='0.0.0.0',
password='postgres',
)
app['db'] = engine
# here we add connection for our injector
postgres_injector.init(engine)
After that you can user postgres_injector to decorate your controllers. For MongoController you don’t need to use ConnectionInjector because connection to db exist in table instance.
Note
If you don’t need to customize some field or add new field in mapper that based on you model then you may don’t put mapper in the controller class. In this case controller will generate this mapper instead of you. Examples which represented below are equals:
from aiohttp_admin2.controllers.postgres_controller import PostgresController from aiohttp_admin2.mappers.generics import PostgresMapperGeneric from aiohttp_admin2.mappers import fields class UserMapper(PostgresMapperGeneric, table=user): """Mapper for user instance.""" @postgres_injector.inject class UserController(PostgresController, table=user): # implicit specify a mapper mapper = UserMapper name = 'user' per_page = 10@postgres_injector.inject class UserController(PostgresController, table=user): name = 'user' per_page = 10
Common settings
access settings
can_create (default True) - True if can to edit an instance
can_update (default True) - True if can to update an instance
can_delete (default True) - True if can to delete an instance
can_view (default True) - True if can to show an instance
If we remove access for some user to some controller then aiohttp admin will automatically hide all url to do this action from interface but if user visit current page directly then admin show error message.
snippet from the demo
class ActorController(PostgresController, table=actors):
mapper = ActorMapper
can_create = False
list settings
inline_fields (default [‘id’]) - list of fields which will show on the list page
snippet from the demo
class ActorController(PostgresController, table=actors):
mapper = ActorMapper
inline_fields = ['id', 'name', 'hash', ]
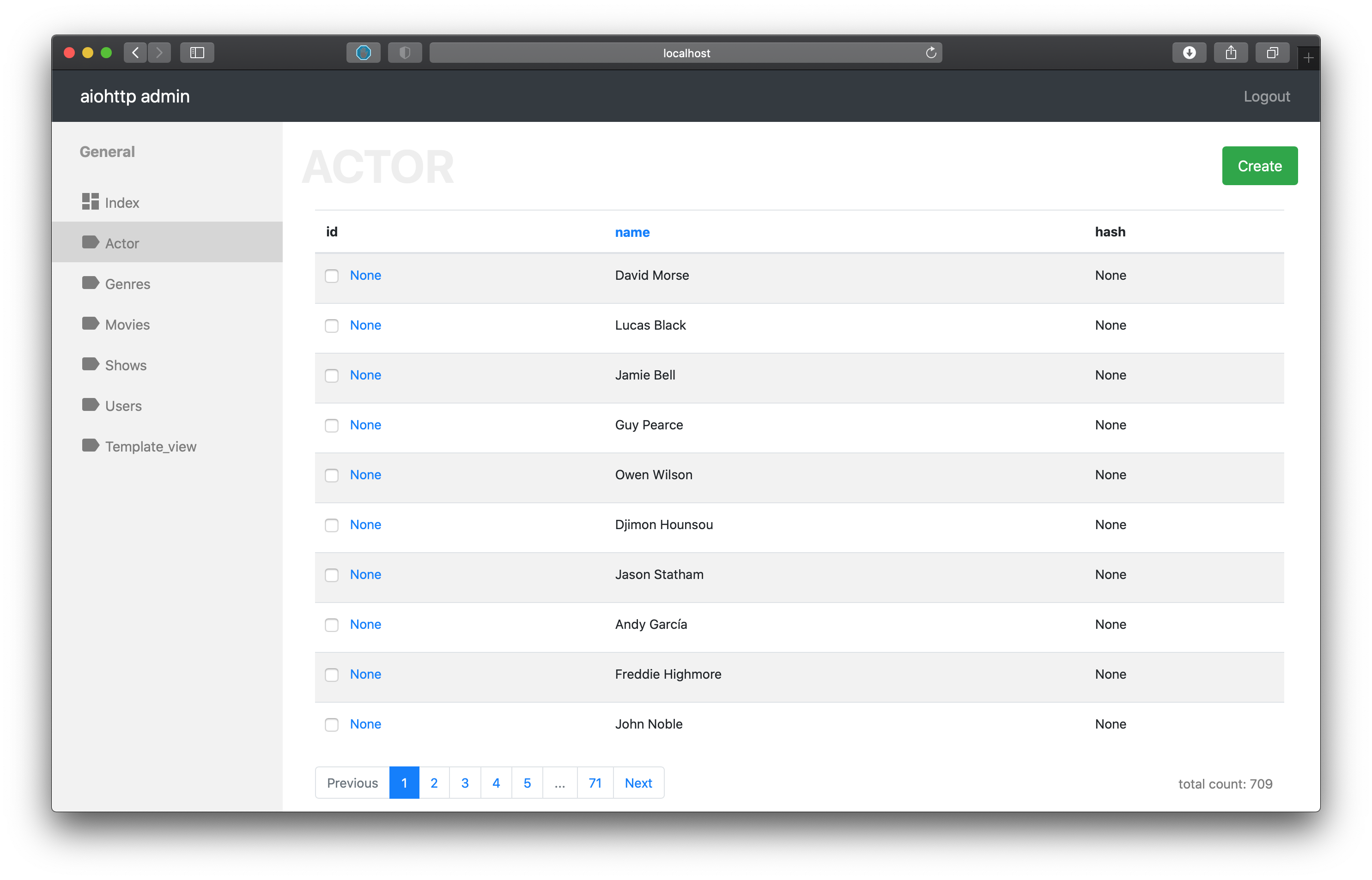
For user on the list page we show only three fields.
search_fields (default []) - list of fields which will use for do search (fields must be searchable)
class ActorController(PostgresController, table=actors):
mapper = ActorMapper
search_fields = ['name', ]
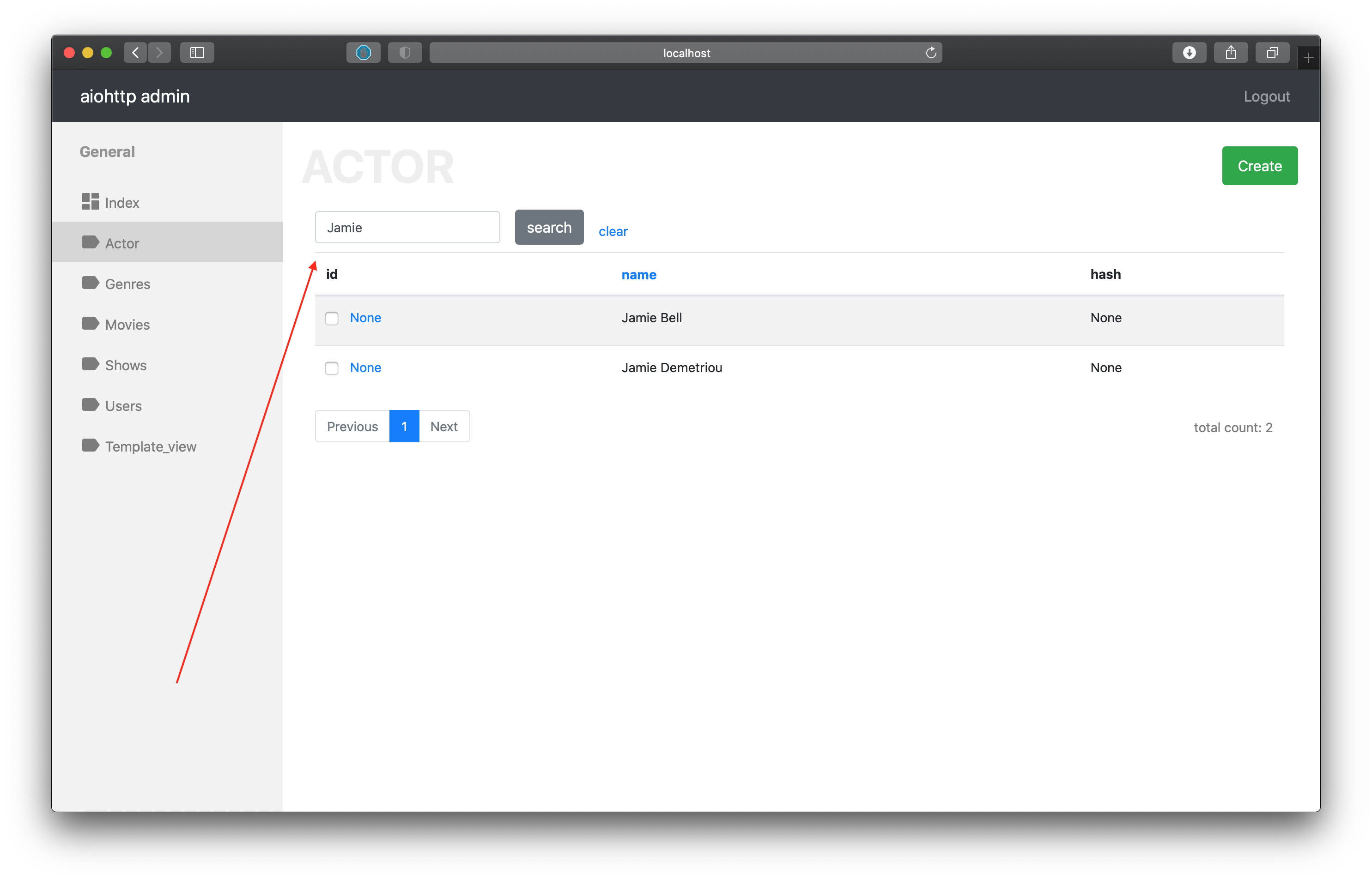
After specify current settings into admin interface you can see search input.
order_by (defaault `id`) - name of field for the default sorting
per_page (defaault `50`) - default count of items per page
list_filter (default []) - list of fields which can to use filters
snippet from the demo
class ActorController(PostgresController, table=actors):
mapper = ActorMapper
inline_fields = ['name', 'gender', ]
list_filter = ['gender', ]
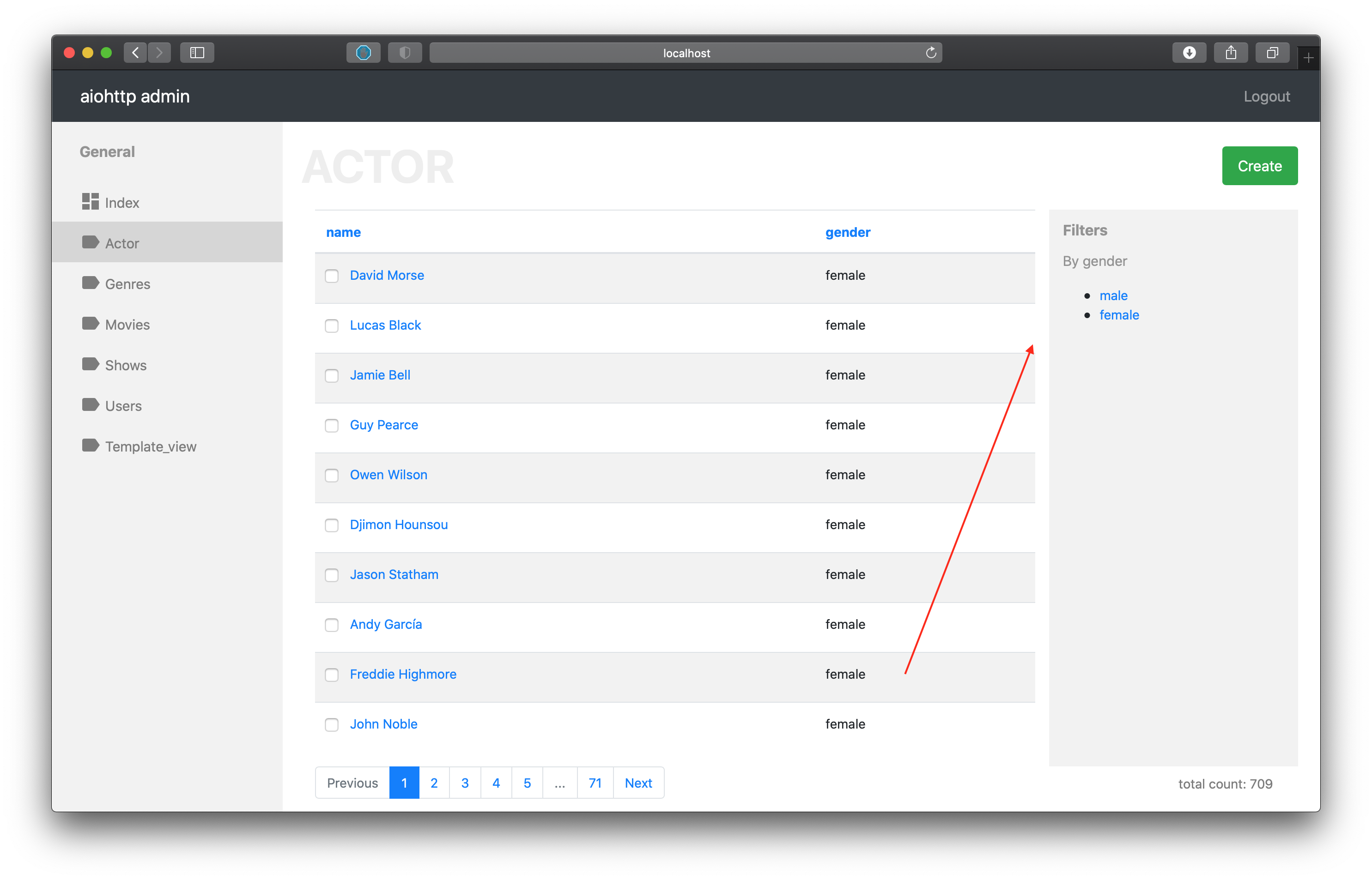
After specify current settings into admin interface you can see filter sidebar with filter for corresponding field.
detail settings
read_only_fields (default []) - list of fields which can’t modify (on the detail page u can see current fields but can’t edit)
exclude_update_fields (default `id`) - list of fields which can’t update (fields will be hide on update page)
exclude_create_fields (default `id`) - list of fields which can’t specify during create a new instance
fields (default `__all__`) - list of available fields
autocomplete_search_fields (default []) - list of feilds which will use to the autocomplete (when you update/create relation fields you just set primary key to input. For improve user experience you can set list of fields which will use to search suggestion items in current input.)
common settings
mapper - a mapper for the current controller
relations_to_one (default []) - list of ToOneRelation which describe one-to-one relation with other controllers
relations_to_many (default []) - list of ToManyRelation which describe many-to-many relation with other controllers
Operations hooks
If you need to do some before/after create/update or delete some data you can use hooks:
pre_create - run before create instance
pre_delete - run before delete instance
pre_update - run before update instance
post_create - run after create instance
post_delete - run after delete instance
post_update - run after update instance
Let’s say that you need to delete key in Redis after delete user instance in PostgeSQL. It might look like this
from aiohttp_admin2.controllers.postgres_controller import PostgresController
from .redis import redis_client
@postgres_injector.inject
class UserController(PostgresController, table=user):
mapper = UserMapper
name = 'user'
async post_delete(self, pk):
await redis_client.delete(f'user:{pk}')
Relations
One-to-one relation
To declare one-to-one relation in aiohttp admin you need to create the ToOneRelation from the aiohttp_admin2.controllers.relations module. Created object you need to add to relations_to_one list in apropriate controller.
snippet from the demo
class ActorMovieController(PostgresController, table=movies_actors):
mapper = ActorMoviesMapper
relations_to_one = [
ToOneRelation(
name='movie_id',
field_name='movie_id',
controller=MoviesController,
),
]
ToOneRelation
name - name of relation
field_name - name of the field which responsible for the current relation
controller - controller of related models (can be callable object)
Many-to-many relation
To declare many-to-many relation in aiohttp admin you need to create the ToManyRelation from the aiohttp_admin2.controllers.relations module. Created object you need to add to relations_to_many list in apropriate controller.
snippet from the demo
class MoviesController(PostgresController, table=movies):
mapper = MoviesMapper
name = 'movies'
relations_to_many = [
ToManyRelation(
name='Actors',
left_table_pk='movie_id',
relation_controller=lambda: ActorMovieController
),
]
ToManyRelation
name - name of relation
left_table_pk - name of the field which responsible for the current relation
relation_controller - controller of related models (can be callable object)
Custom fields
On list page you can add custom fields or rewrite view of existing. Let’s consider case from the demo related with image representation. Each movie has a picture url but on list page view want to show image block.
snippet from the demo
from markupsafe import Markup
class MoviesController(PostgresController, table=movies):
mapper = MoviesMapper
name = 'movies'
inline_fields = ['poster', 'title', ]
async def poster_field(self, obj):
return Markup('<img src="{path}" width="100">')\
.format(path=obj.data.poster_path)
For that into inline_fields we add new field poster and create a function poster_field (<field_name>_field) which receive as second argument the current Instance object. Also for give access use html in field without escaping we need to wrap our html in a Markup object.
To get the field value from the Instance object, we need to get the data property and try to get the field which we need.
async def poster_field(self, obj):
return obj.data.poster_path
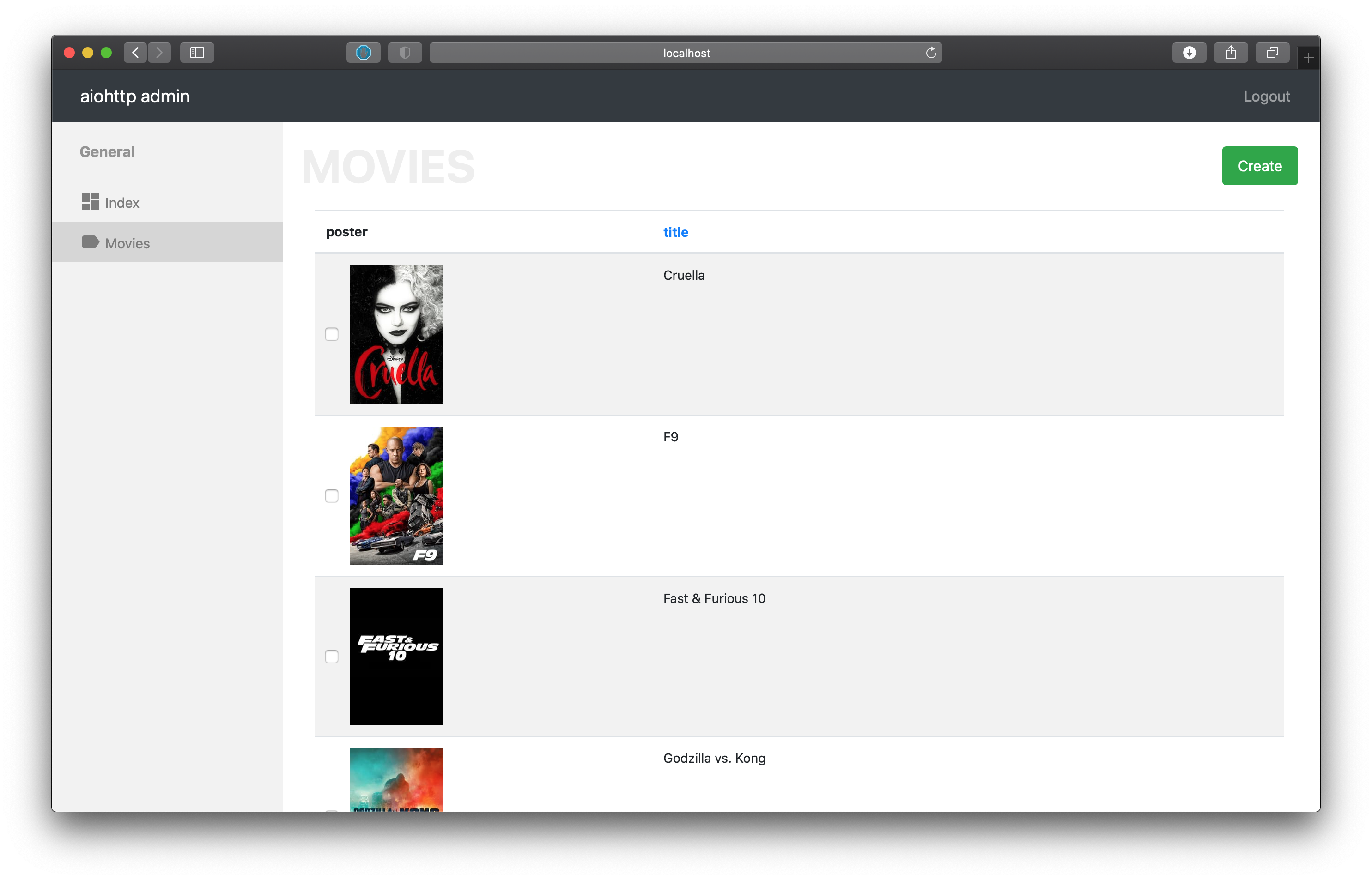
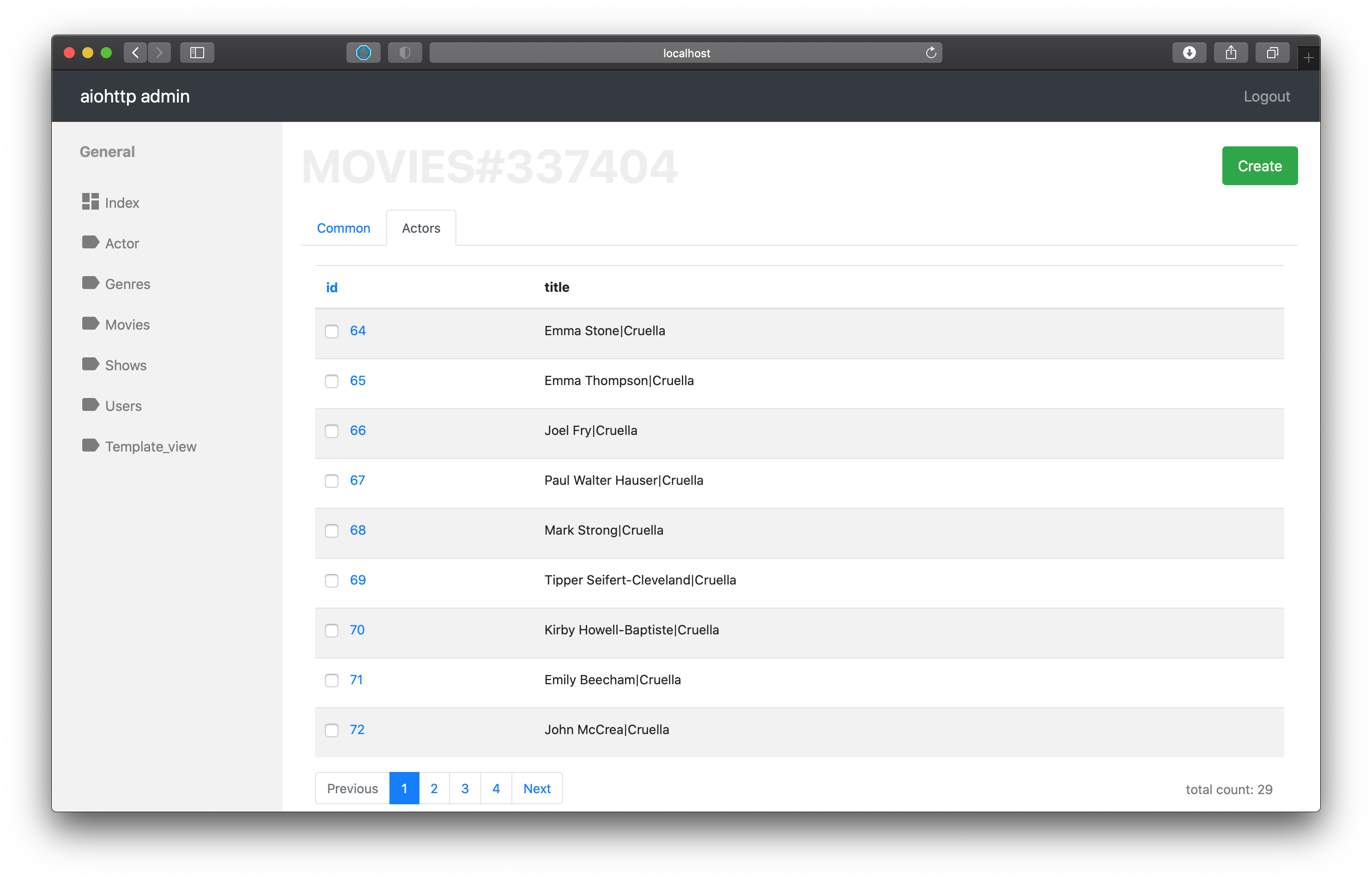
Also you can to get relation instances inside custom fields, for that just use get_relation method of Instance class to get related Instance object from other controller.
from aiohttp_admin2.controllers.relations import ToOneRelation
class ActorMovieController(PostgresController, table=movies_actors):
mapper = ActorMoviesMapper
inline_fields = ['id', 'title', ]
relations_to_one = [
ToOneRelation(
# relation name
name='movie_id',
field_name='movie_id',
controller=MoviesController,
),
ToOneRelation(
# relation name
name='actor_id',
field_name='actor_id',
controller=ActorController,
),
]
async def title_field(self, obj):
# get via relation name
actor = await obj.get_relation('actor_id')
# get via relation name
movie = await obj.get_relation('movie_id')
return actor.data.name + "|" + movie.data.title
Custom sort
To specify custom sorting we need to provide sort method into contorller class for the current field (<field_name>_sort). This function receive is_reverse that mean need we return reverse sorting or not.
In example below we add custom field which from json field data get key and implement sorting for this field in the data_field_sort method.
@postgres_injector.inject
class UsersController(PostgresController, table=users):
mapper = UsersMapper
inline_fields = ['id', 'data', ]
async def data_field(self, obj) -> str:
if obj.data.payload and isinstance(obj.data.payload, dict):
return obj.data.data
return ''
def data_field_sort(self, is_reverse):
if is_reverse:
return sa.text("payload ->> 'data' desc")
return sa.text("payload ->> 'data'")
Views
This class use for represent data on the admin interface. The simples view which you can to create is TemplateView.
TemplateView
from aiohttp_admin2.view import TemplateView
class NewPage(TemplateView):
title = 'new page'
template_name = 'aiohttp_admin/my_template.html'
You can change specify template for you custom view as in example above or specify content variable in jinja’s context.
from aiohttp_admin2.view import TemplateView
class NewPage(TemplateView):
title = 'new page'
async def get_context(self, req):
return {
**await super().get_context(req=req),
"content": "My custom content"
}
template_name - path to template for current page
Dashboards view is just subclass of TemplateView which you can to customize in the same way.
Common settings
All view has properties which describe below:
is_hide_view - if we don’t want to show link on current views in the aside bar then we need to set True
group_name - If views have the same group name then they will organize together into separate block in the aside bar
name - This string will use as the pretty name of the current views in the admin interface.
We can to see how below settings work together
from aiohttp_admin2.views import TemplateView
class FirstView(TemplateView):
group_name = 'first group'
name = 'first view'
class SecondView(TemplateView):
group_name = 'first group'
name = 'second view'
class ThirdView(TemplateView):
group_name = 'second group'
name = 'third view'
class FourthView(TemplateView):
group_name = 'second group'
name = 'fourth view'
class FifthView(TemplateView):
group_name = 'second group'
name = 'fifth view'
# hide current view
is_hide_view = True
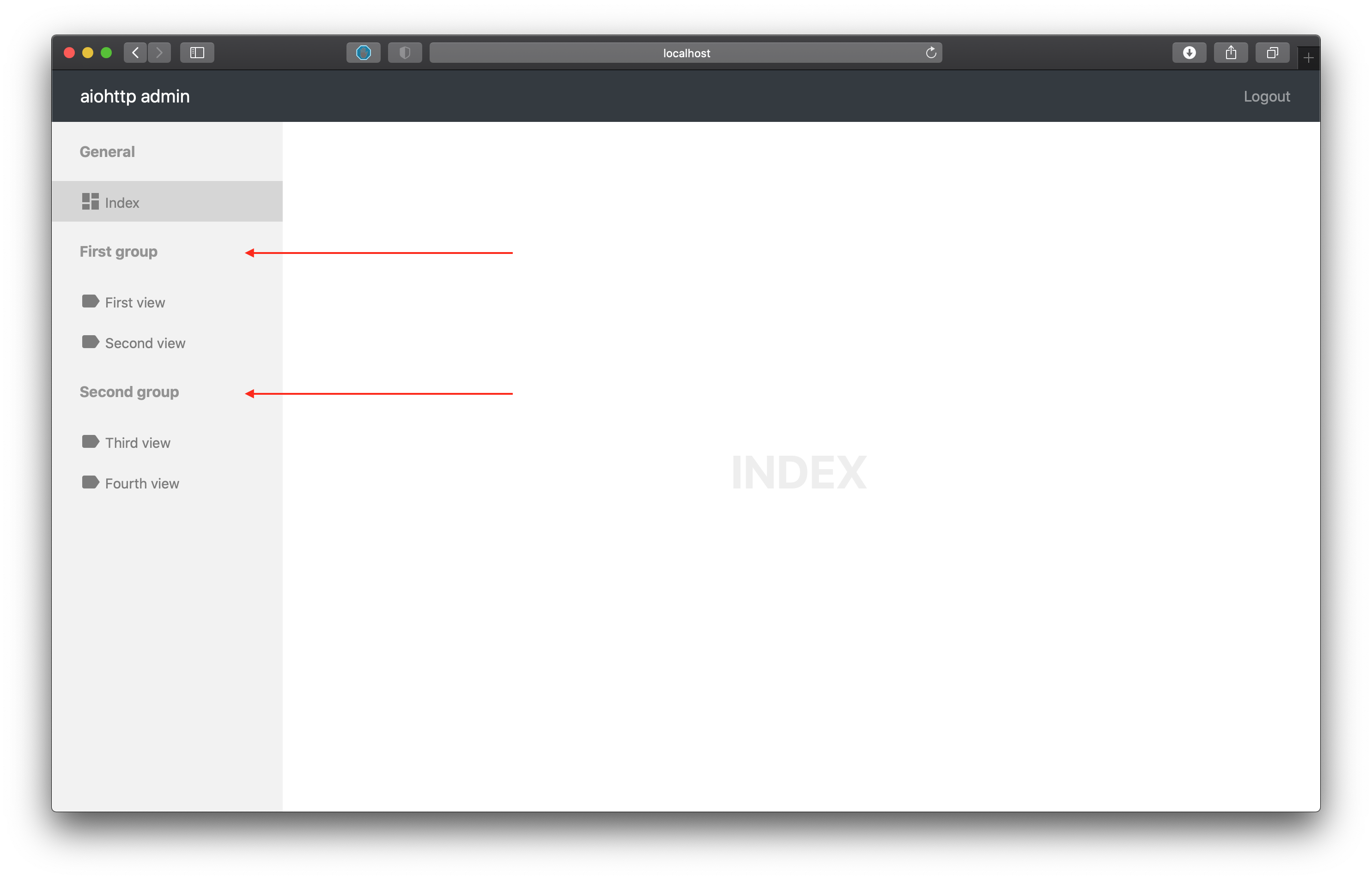
We can see that first and second views concat in single group in a side menu because common group_name and the same story with third and fourth views but fifth doesn’t exist in menu because the view has is_hide_view setting set to True.
index_url - The url prefix path for all routes related with the current views
icon - This string set a type of icon which will use in aside bar for the current views (full list of available icons you can to find here)
ControllerView
Controller view is view for representation information related with your models.
from aiohttp_admin2.view import ControllerView
class UserView(ControllerView):
controller = UserController
You can specify templates which you wanna use for instead of default:
template_list_name - the template for list page (with a simple pagination)
template_list_cursor_name - the template for list page (with an infinite scroll)
template_detail_name - the template for detail page in read only mode
template_detail_edit_name - the template for detail page in edit mode
template_detail_create_name - the template for create page
template_delete_name - the template for delete page
also you can to specify:
infinite_scroll (True/False default False) - if set to True then will use infinite scroll instead of standard pagination. It can be very helpful when table is so large and count query (which need to generate standard pagination bar) is so cost.
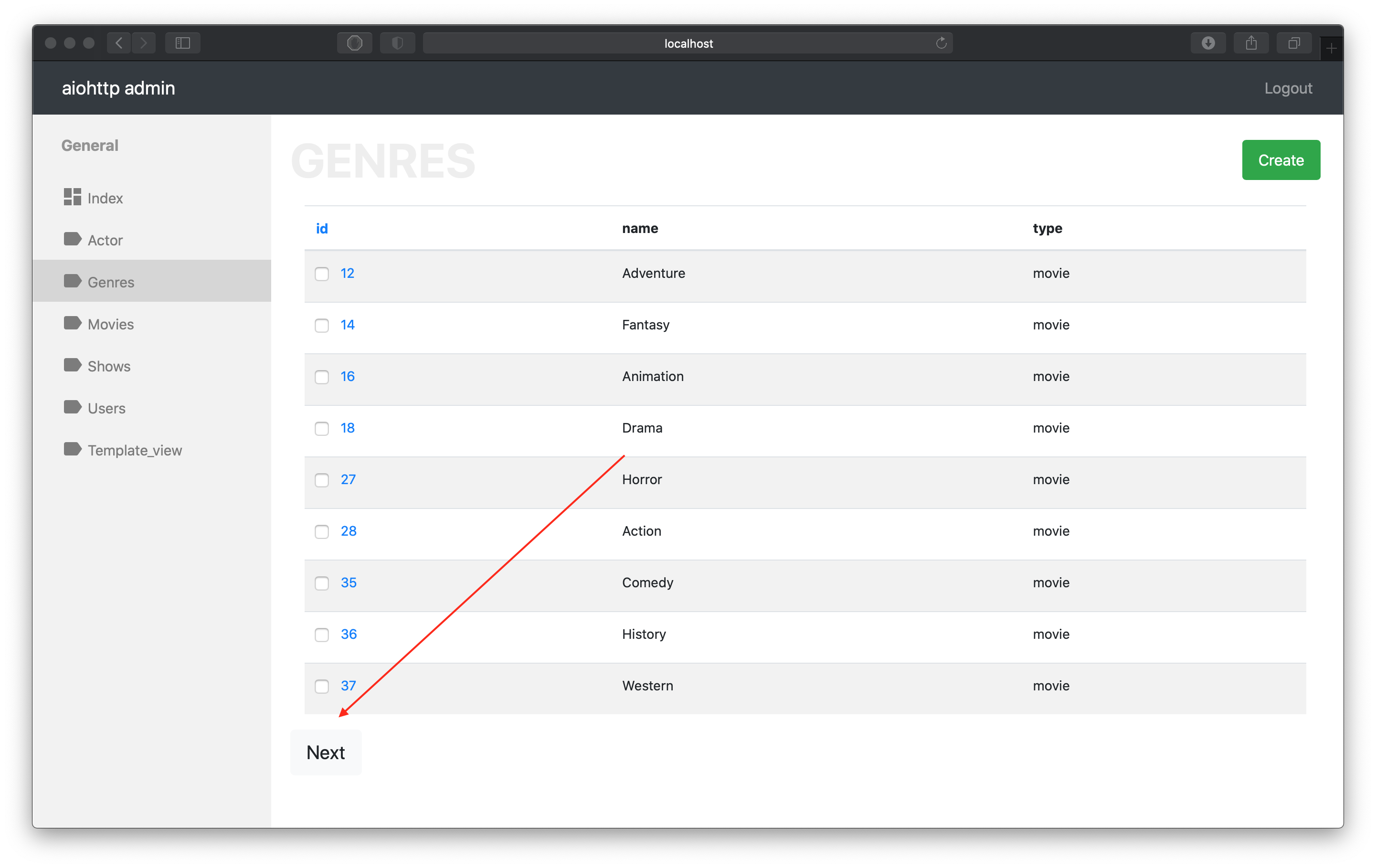
After specify current setting to True we can to see that standard pagination bar has been replaced by Next button.
search_filter (default SearchFilter) - filter which will use for search (for search input at the top of list page)
fields_widgets (default empty dict) - a map of field names and coresponding widngets. It’s helpful if you want to specify a some special widget for the particular field.
type_widgets (default empty dict) - a map of field type and coresponding widngets. It’s helpful if you want to specify a some special widget for the particular type of field.
foreignkey_widget (default AutocompleteStringWidget) - a widget which will use for the autocomplete
View’s Widgets and Filters
The widgets and filters class need only to allocated path to the template and extra .css and .js files which need to corrected render of it. Custom widget have to inherit from BaseWidget. Custom filter have to inherit from FilerBase.
Custom Routes
You can use @route decorator to add custom endpoint to your view
from aiohttp_admin2.view import ControllerView
from aiohttp_admin2.views.aiohttp.views.utils import route
class UserView(ControllerView):
controller = UserController
@route(r'/{pk:\d+}/ban/', method='POST')
def ban_user(self, req):
# ban_user(req.match_info['pk'])
return await self.get_detail(req)
@route takes 2 parameters: url and method. Valid methods are: POST, GET, PUT, DELETE, HEAD. The URL must always start and end with /.
Templates
For generate pages aiohttp_admin use jinja2.
If you setup aiohttp_jinja2 with not default jinja_app_key argument then you should initialize admin interface with your jinja_app_key argument.
aiohttp_admin.setup_admin(app, jinja_app_key='my_jinja_value')
Overriding jinja templates
You can rewrite native templates for aiohttp_admin. For that you should create aiohttp_admin directory into templates’s directory for the jinja2 and create your template with name of template witch you want to rewrite.
The full list of templates you can see below:
aiohttp_admin/blocks/header.html - the header for base layout
aiohttp_admin/layouts/base.html - the base layout
aiohttp_admin/layouts/create_page.html - the content for create page
aiohttp_admin/layouts/delete_page.html - the content for confirm delete page
aiohttp_admin/layouts/detail_view_page.html - the content for detail page in read only mode
aiohttp_admin/layouts/detail_edit_page.html - the content for edit page
aiohttp_admin/layouts/custom_page.html - the content for custom page
aiohttp_admin/layouts/custom_tab_page.html - the content for custom tab
aiohttp_admin/layouts/list_page.html - the content for list page (with a simple pagination)
aiohttp_admin/layouts/list_cursor_page.html - the content for list page (with an infinite scroll)
aiohttp_admin/blocks/from/form.html - the main form for create and update
aiohttp_admin/blocks/from/field_errors.html - the macro for form’s errors
aiohttp_admin/blocks/from/field_title.html - the macro for form’s title
aiohttp_admin/blocks/from/fields/* - the macros for different types of fields
aiohttp_admin/blocks/filters/* - the macros for different types of filters (in the left aside bar)
aiohttp_admin/blocks/pagination.html - the pagination block
aiohttp_admin/blocks/cursor_pagination.html - the infinity scroll pagination block
aiohttp_admin/blocks/list_action_buttons.html - the list actions for list page
aiohttp_admin/blocks/list_cell.html - the macro for table cell
aiohttp_admin/blocks/list_objects_block.html - the table for list page
aiohttp_admin/blocks/list_objects_header_block.html - the header of table for list page
aiohttp_admin/blocks/messages.html - the macro for message’s notification bar
aiohttp_admin/blocks/nav_aside.html - the aside with pages links
aiohttp_admin/blocks/tabs_bar.html - the template for tabs
Overriding view templates
You also can specify template for some special ControllerView.
class UserPage(ControllerView):
controller = UserController
template_list_name = 'aiohttp_admin/layouts/list_page.html'
template_list_cursor_name = 'aiohttp_admin/layouts/list_cursor_page.html'
template_detail_name = 'aiohttp_admin/layouts/detail_view_page.html'
template_detail_edit_name = 'aiohttp_admin/layouts/detail_edit_page.html'
template_detail_create_name = 'aiohttp_admin/layouts/create_page.html'
template_delete_name = 'aiohttp_admin/layouts/delete_page.html'
Resources
So, we already told that Resources is a class which implement method to work with some particular database. If you want to implement your own Resources you need just inherit from AbstractResource and implement methods which described below:
get_one - Get one an instance from a storage. This method receive primary key of an database’s object and return the Instance if object exist else raise the InstanceDoesNotExist exception.
get_many - Get many instances by ids from a storage. This method will use as a dataloader. This method mainly will use on list page in cases when need to show field with data from related model for prevent N + 1. This method receive list of primary keys of an database’s objects and name of primary key after that return dict where keys are primary keys and as a values corresponding Instance objects (InstanceMapper).
delete - Delete instance. This method receive primary key of instance and delete it or raise the InstanceDoesNotExist exception if object doesn’t exist.
create - Create instance. This method receive Instance object and return it from databases after create.
update - Update instance. This method receive primary key and Instance object after that update an object in databases and return corresponding Instance object.
get_list - Get list of instances. This method will use for show list of instances. The current method have to implement possible to pagination, filtering and sorting.
PostgresResource
get_list_select - In this method you can redefine query. It might helpful when you need to use need to do join or add to response a field based on some aggregation
Filters
For filtering data resources use Filters objects. Filter object can apply condition expressions to query. Each filter inherit from ABCFilter class and provide apply method which will apply to query conditions.